Amniotic Fluid Disorders: 25 Hard Case-Based MCQs | Oligohydramnios & Polyhydramnios Exam Practice 2025
 ---
---
# ⭐ **AMNIOTIC FLUID – COMPLETE MASTER REFERENCE**
---
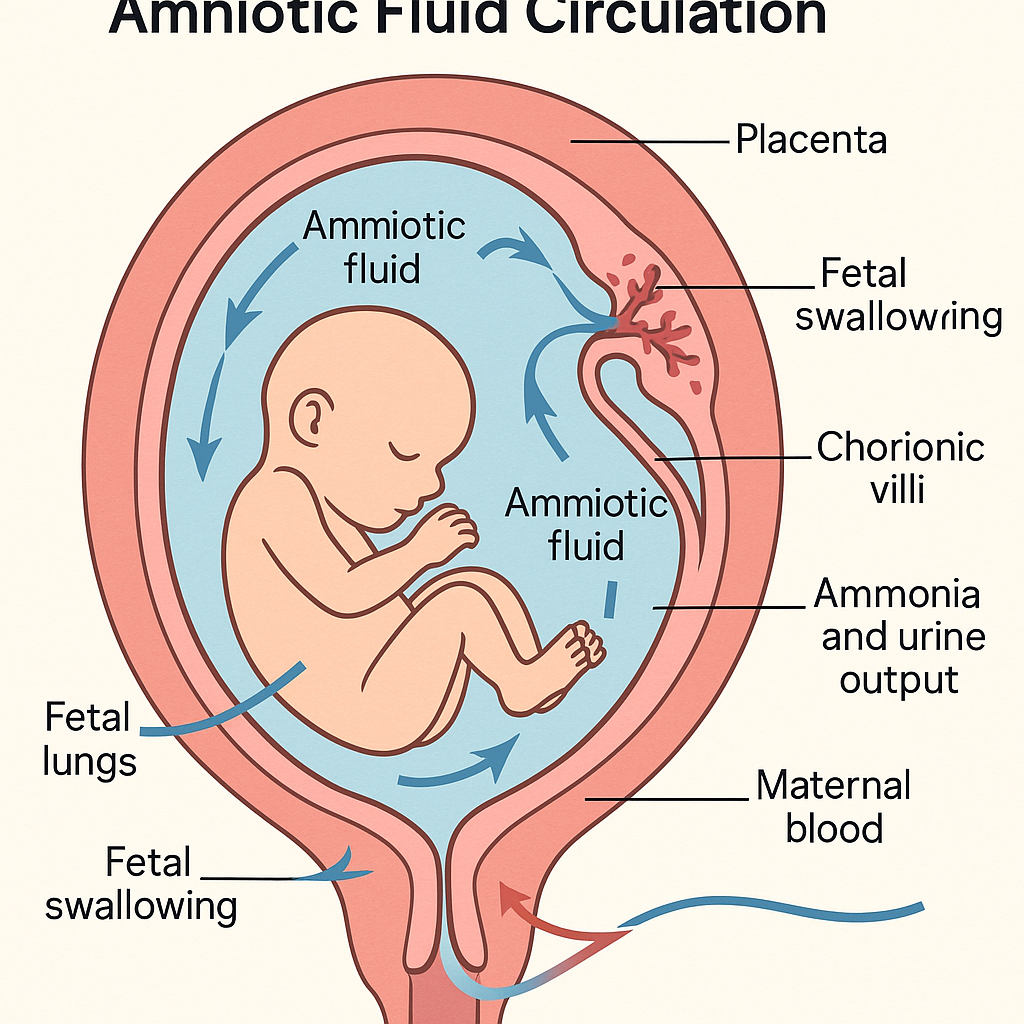
## **1. What is Amniotic Fluid?**
Amniotic fluid (AF) is the **protective liquid** within the amniotic sac that surrounds the fetus.
### **Functions**
* Cushioning → prevents trauma
* Allows fetal movement → musculoskeletal development
* Prevents cord compression
* Maintains temperature
* Enables lung development → fetal breathing movements
* Prevents adhesions of membranes
* Facilitates exchange of nutrients, water, biochemical products
---
## **2. Sources of Amniotic Fluid (Based on Gestation Age)**
### **First Trimester**
* **Amnion + maternal plasma transudate**
* Chorionic membrane diffusion
### **Second Trimester**
* **Fetal urine (major source)**
* Fetal lung secretions
* Transmembranous & intramembranous pathways
* Fetal swallowing regulates AF volume
### **Third Trimester**
* **Fetal urine = 700–900 mL/day**
* Fetal swallowing = AF removal
* The balance determines AFV
---
# ⭐ **3. Colors of Amniotic Fluid & Their Clinical Meaning**
| **Color** | **Meaning / Cause** |
| ------------------ | ---------------------------------------------------- |
| **Clear** | Normal |
| **Greenish** | *Meconium-stained fluid* → fetal distress, post-term |
| **Yellow** | *Hemolysis* (Rh isoimmunization), bilirubin |
| **Dark brown** | *Old meconium*, fetal demise |
| **Red / bloody** | Placental abruption, vasa previa rupture |
| **Straw-colored** | Chorioamnionitis sometimes |
| **Golden-colored** | Severe hemolytic disease |
| **Milky white** | Vernix |
---
# ⭐ **4. Assessments of Amniotic Fluid**
## **4.1 AFI (Amniotic Fluid Index)**
Sum of vertical pockets in 4 quadrants.
| **AFI Value** | **Interpretation** |
| ------------- | ------------------ |
| **< 5 cm** | Oligohydramnios |
| **5 – 8 cm** | Borderline low |
| **8 – 24 cm** | Normal |
| **> 24 cm** | Polyhydramnios |
---
## **4.2 Single Deepest Vertical Pocket (SDVP)**
* **< 2 cm** = Oligohydramnios
* **2–8 cm** = Normal
* **> 8 cm** = Polyhydramnios
**Preferred in multiple pregnancies.**
---
# ⭐ **5. AMNIOTIC FLUID DISORDERS**
---
# **A. Oligohydramnios**
### **Definition**
* **AFI < 5 cm**
* **SDVP < 2 cm**
### **Causes**
#### *Fetal*
* Renal agenesis (Potter sequence)
* PCKD
* Posterior urethral valves
#### *Placental*
* Uteroplacental insufficiency
* Preeclampsia
* Post-term pregnancy
#### *Maternal*
* ACE inhibitors
* NSAIDs
* Dehydration
#### *Others*
* **PPROM** (most common in third trimester)
---
### **Investigations**
* USG → AFI/SDVP
* Doppler → Placental insufficiency
* Anomaly scan → Renal system
* NST / BPP for fetal well-being
* Check maternal BP, proteinuria
---
### **Management**
**Depends on Cause + GA:**
#### **1. < 34 weeks**
* Hydration (oral + IV)
* Stop ACE-I / NSAIDs
* Doppler surveillance
* For PPROM → antibiotics + steroids
* Expectant management
#### **2. 34–37 weeks**
* If stable, close monitoring
* Consider induction if fetal distress or severe oligohydramnios
#### **3. ≥ 37 weeks**
* **Induction of labor**
#### **Intrapartum**
* **Amnioinfusion** for recurrent variable decelerations
---
# **B. Polyhydramnios**
### **Definition**
* AFI > 24 cm
* SDVP > 8 cm
---
### **Causes**
#### Fetal:
* Anencephaly / Open NTD
* Esophageal atresia
* Duodenal atresia (“double bubble”)
* High-output cardiac failure
* Twin–twin transfusion syndrome (TTTS)
#### Maternal:
* Diabetes mellitus
* Rh isoimmunization
#### Placental:
* Chorioangioma
---
### **Investigations**
* USG → AFI, anomalies
* Glucose challenge test
* Doppler if fetal anemia suspected
* TORCH IgM if infection suspected
---
### **Management**
#### **Mild (Most common)**
* Observation
* Serial USG
#### **Moderate–Severe**
* **Indomethacin 25 mg q6h** (ONLY < 32 weeks)
* **Amnioreduction**
* Treat underlying cause
* Control maternal diabetes
* TTTS → fetoscopic laser ablation
#### **Delivery**
* Indications:
* Fetal compromise
* Maternal distress
* Severe polyhydramnios
Risk of **cord prolapse**, **malpresentation**.
---
# 🔥 **NOW — 30 HIGH-YIELD CASE SCENARIOS WITH MANAGEMENT**
---
# ⭐ **Case Scenarios 1–10: Oligohydramnios**
### **Case 1**
A 32-week G2P1 mother with severe preeclampsia has AFI = 3 cm. Doppler shows high resistance in umbilical artery.
**Diagnosis:** Placental insufficiency–related oligohydramnios
**Management:**
* Admit
* Steroids
* Daily NST
* Deliver if absent/reversed EDF
---
### **Case 2**
28 weeks, PPROM, AFI 2 cm.
**Management:**
* Antibiotics
* Steroids
* Expectant management
* Deliver if chorioamnionitis or fetal distress
---
### **Case 3**
38 weeks, AFI 4 cm, NST reactive.
**Management:**
* Induce labor (term oligohydramnios)
---
### **Case 4**
22-week anomaly scan → Bilateral renal agenesis, absent bladder filling, severe oligohydramnios.
**Likely diagnosis:** Potter sequence
**Management:**
* Counsel → incompatible with life
* Option for termination
---
### **Case 5**
41-week post-term pregnancy, AFI = 4 cm.
Management: Induction due to placental insufficiency
---
### **Case 6**
G1 mother on ACE inhibitors (enalapril). AFI 3 cm.
Management:
* STOP ACE-I immediately
* Hydration
* Monitor AFI
---
### **Case 7**
Pregnant woman with dehydration from vomiting; AFI 5 → 8 cm after hydration.
Management: Rehydration therapy
---
### **Case 8**
Intrapartum oligohydramnios with recurrent variable decelerations.
Management: **Amnioinfusion**
---
### **Case 9**
PPROM + fever + foul-smelling discharge. AFI 2 cm.
Diagnosis: Chorioamnionitis
Management: Immediate delivery + IV antibiotics
---
### **Case 10**
32 weeks → IUGR + AFI 3 + BPP 4/10.
Management: Deliver (non-reassuring fetal status)
---
# ⭐ **Case Scenarios 11–20: Polyhydramnios**
### **Case 11**
GDM mother, AFI = 28 cm, fetus large for gestational age.
Management:
* Control sugars
* NST / BPP surveillance
* Deliver at term
---
### **Case 12**
20 weeks, AFI 32 cm, USG shows absent stomach bubble.
Diagnosis: Esophageal atresia
Management:
* Refer to fetal medicine
* Counsel
* Plan postnatal surgery
---
### **Case 13**
34 weeks, severe polyhydramnios + maternal dyspnea.
Management:
* Therapeutic amnioreduction
* Rule out anomalies
---
### **Case 14**
28 weeks, AFI 35 cm, monochorionic twins with discordant growth.
Diagnosis: TTTS
Management: Fetoscopic laser ablation
---
### **Case 15**
20-week fetus with anencephaly + polyhydramnios.
Management: Discuss termination options
---
### **Case 16**
Rh isoimmunization → MCA PSV high → fetal anemia + polyhydramnios.
Management: Intrauterine transfusion
---
### **Case 17**
UTI in pregnancy + mild polyhydramnios.
Management: Treat infection; repeat scan
---
### **Case 18**
Chorioangioma on placenta + polyhydramnios.
Management: Monitor + possible laser coagulation
---
### **Case 19**
35 weeks → fetal hydrops + AFI 30 cm.
Management: Investigate cause (Rh, infection) + possible early delivery
---
### **Case 20**
32-week mother with severe reflux due to polyhydramnios.
Management: Amnioreduction + symptomatic therapy
---
# ⭐ **Case Scenarios 21–30: Mixed, Advanced, Exam-Level**
### **Case 21**
Severe IUGR + oligohydramnios + absent diastolic flow.
Action: Immediate delivery ( > 32 weeks )
---
### **Case 22**
Pregnancy with lupus nephritis flare → oligohydramnios.
Management: Treat maternal disease + surveillance
---
### **Case 23**
Polyhydramnios after uncontrolled diabetes, AFI improved after insulin optimization.
Interpretation: Reversible cause
---
### **Case 24**
Borderline AFI (6 cm) and reduced fetal movement.
Management: NST + repeat AFI in 24 hours
---
### **Case 25**
Post-amniocentesis fluid leakage → oligohydramnios.
Management: Expectant + hydration
---
### **Case 26**
36 weeks, breech + polyhydramnios.
Risk: Cord prolapse
Management: Elective C-section
---
### **Case 27**
Term pregnancy + thick meconium-stained fluid.
Interpretation: Fetal distress
Management: Continuous FHR monitoring; prepare for neonatal resuscitation
---
### **Case 28**
Fetus has duodenal atresia ("double bubble") + AFI 30.
Management: Delivery at tertiary center + neonatal surgery
---
### **Case 29**
AFI normal earlier; now sudden drop to AFI 3.
Rule out: PPROM
Test: Nitrazine/ferning/IGFBP-1
---
### **Case 30**
Suspected polyhydramnios, but SDVP = 6 cm (normal).
Interpretation: AFI misleading; SDVP more accurate
---HTML Versions
