Home
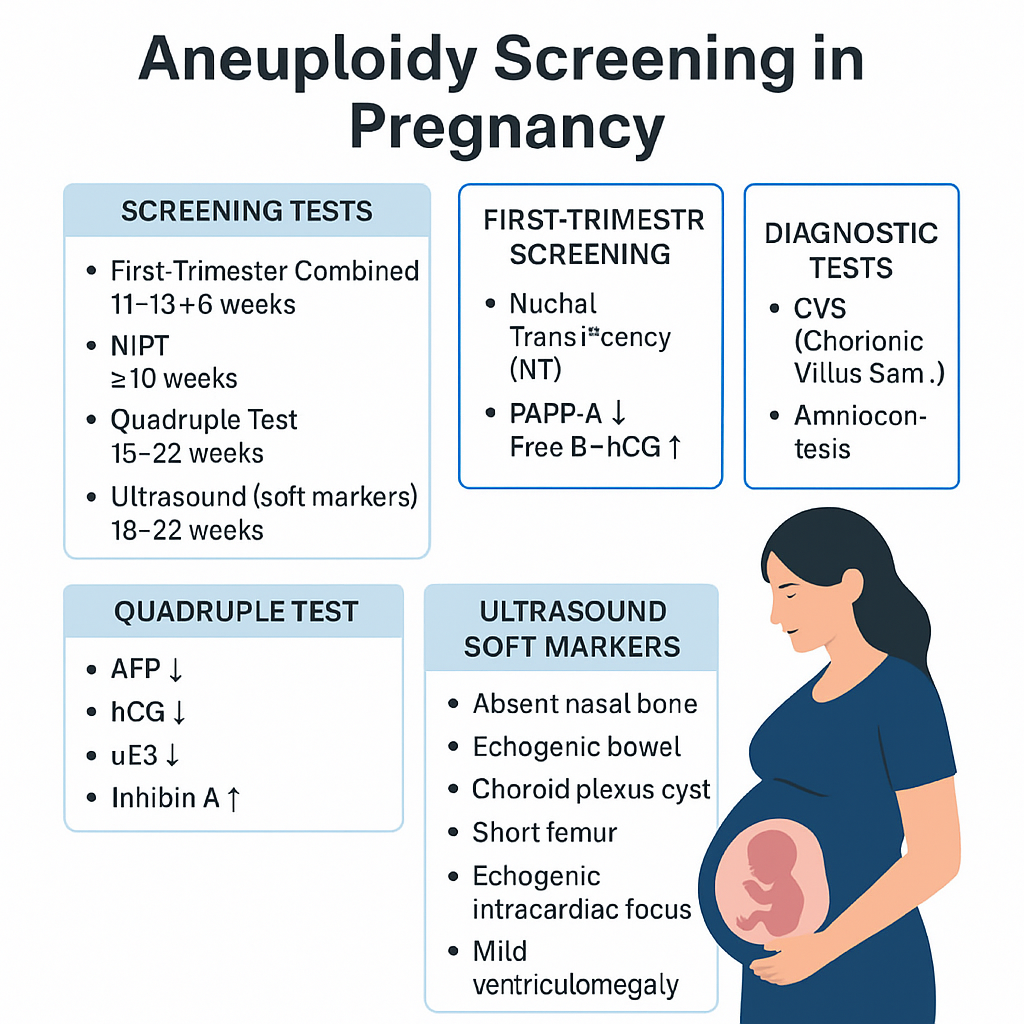
Aneuploidy Screening in Pregnancy: First Trimester, Quadruple Test, NIPT & Soft Markers | Complete Guide 2025 --- HTML Versions