Home
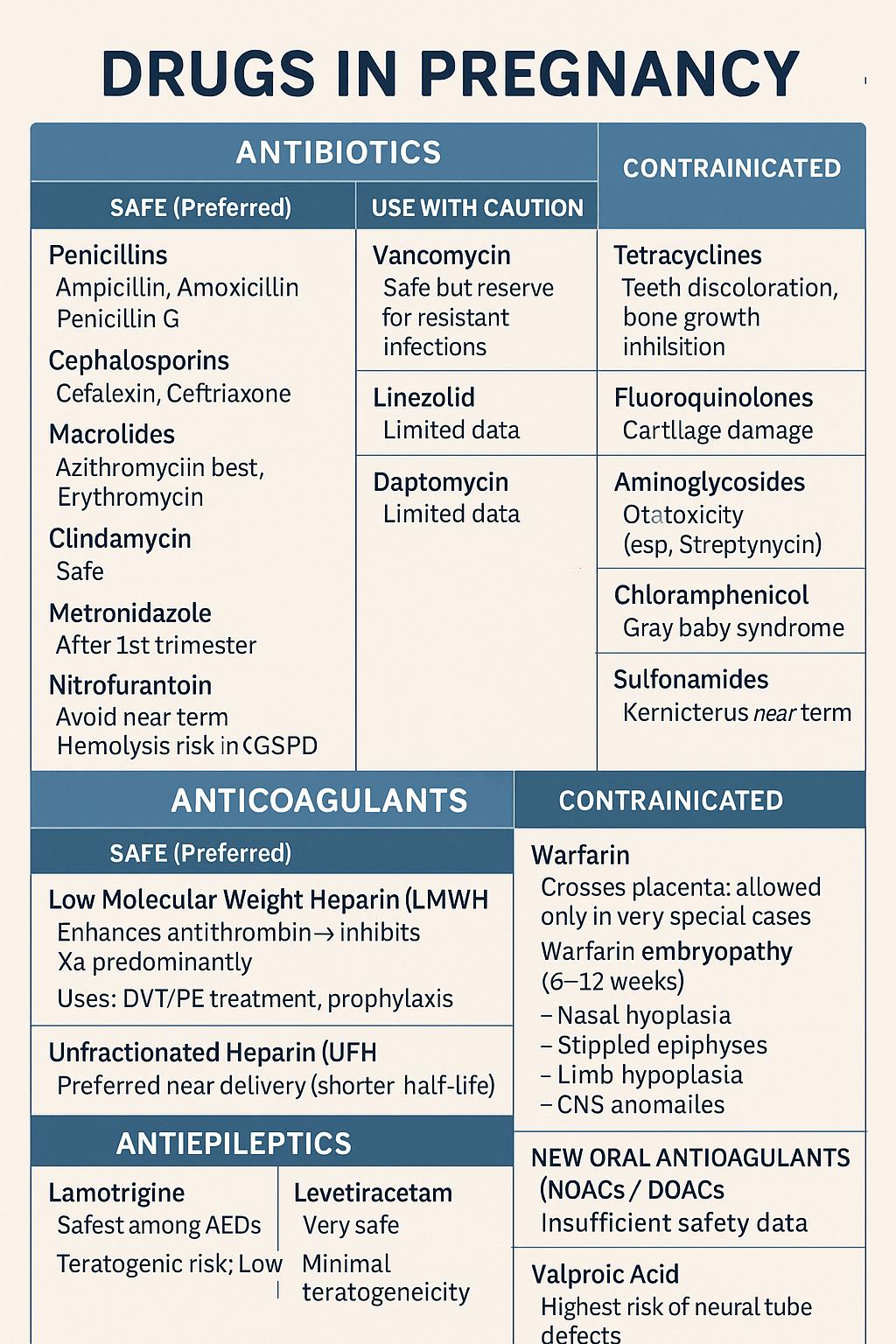
Comprehensive guide on safe and unsafe drugs in pregnancy including antibiotics, anticoagulants, and antiepileptics. Covers risks, teratogenicity, and clinical management Below is a **concise but complete, exam-ready note** on **Drugs in Pregnancy – Antibiotics, Anticoagulants, Antiepileptics**. HTML Versions