Home
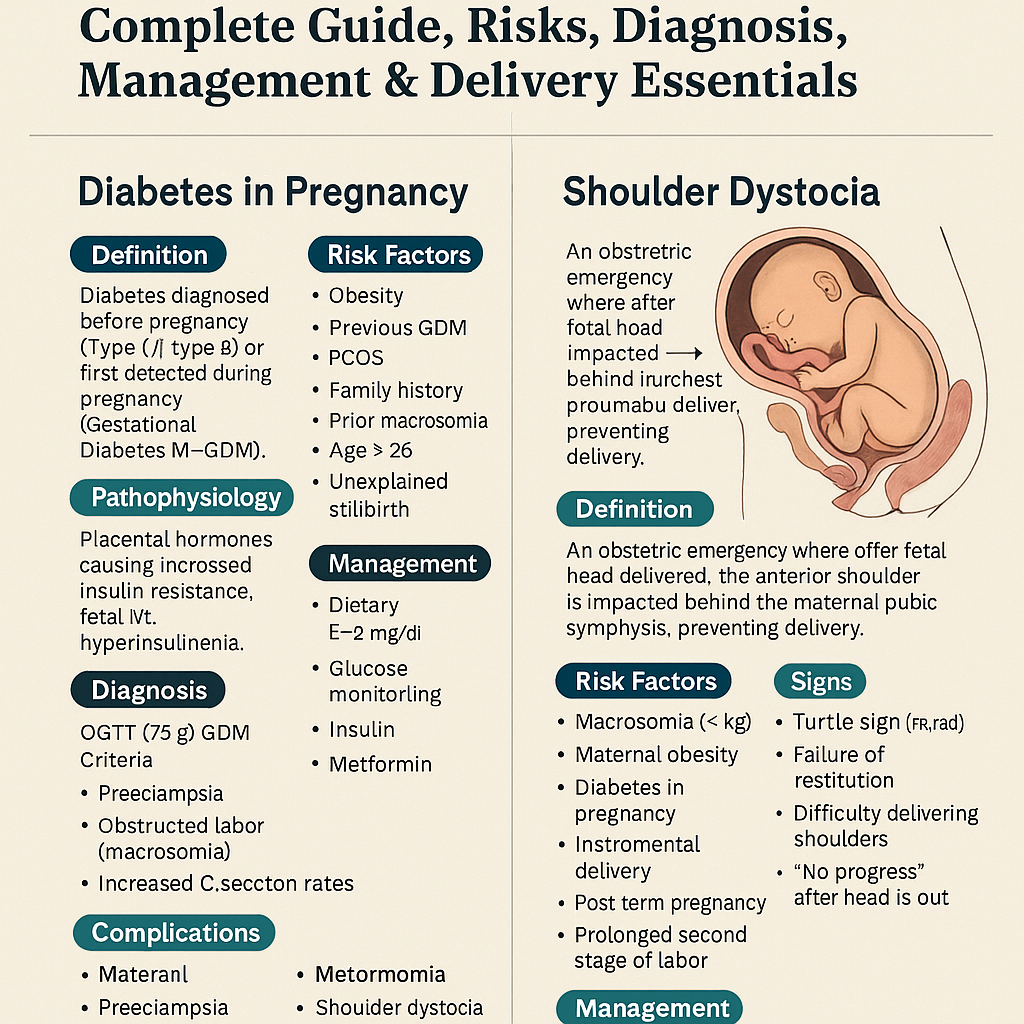
Diabetes in Pregnancy & Shoulder Dystocia – Complete Guide, Risks, Diagnosis, Management & Delivery Essentials Below is a **stylish, concise-but-complete medical reference** on **Diabetes in Pregnancy** and **Shoulder Dystocia**, written in an exam-ready, high-yield format with clean headings and clinical depth. HTML Versions