Home
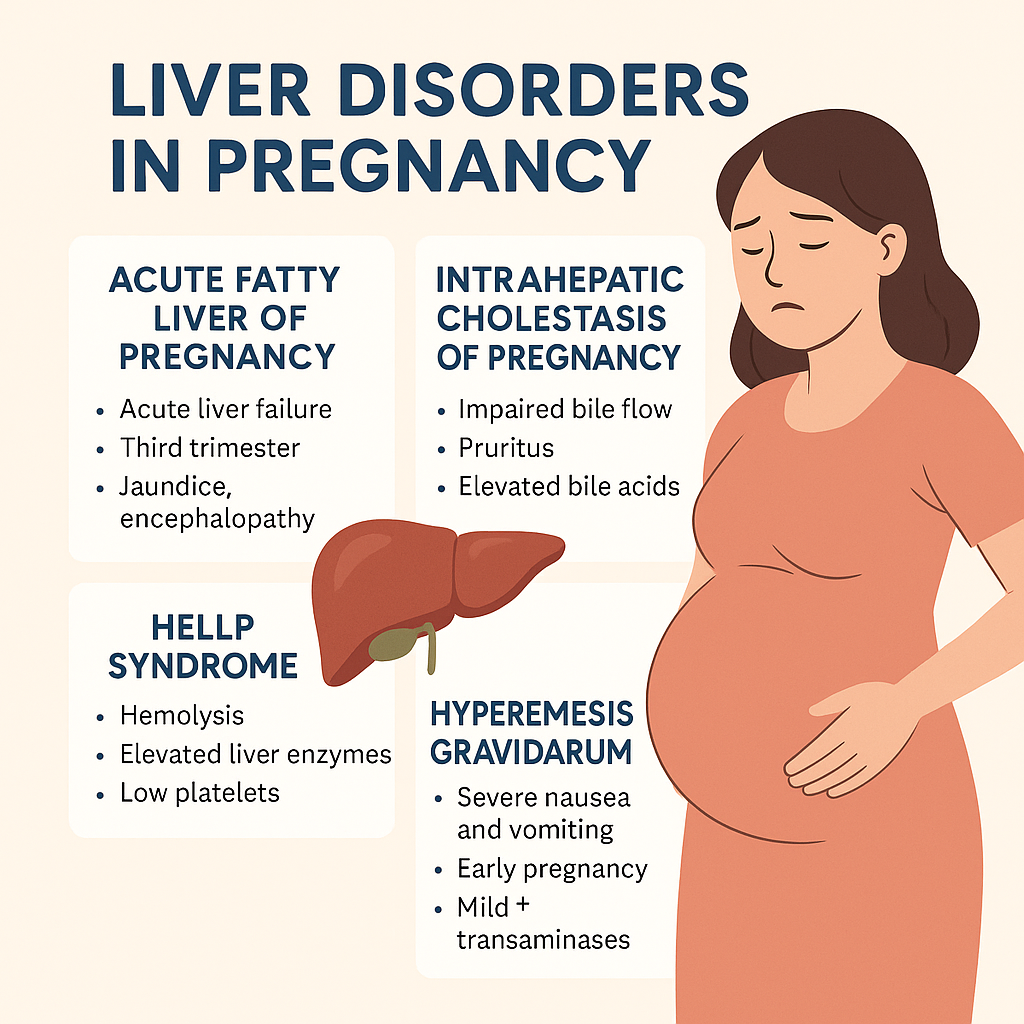
Liver Disorders in Pregnancy: Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis & Management | Complete Guide 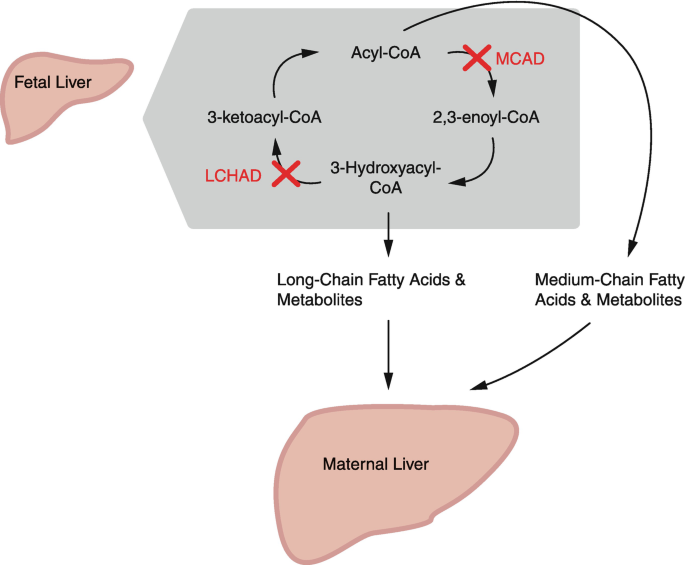 HTML Versions