Home
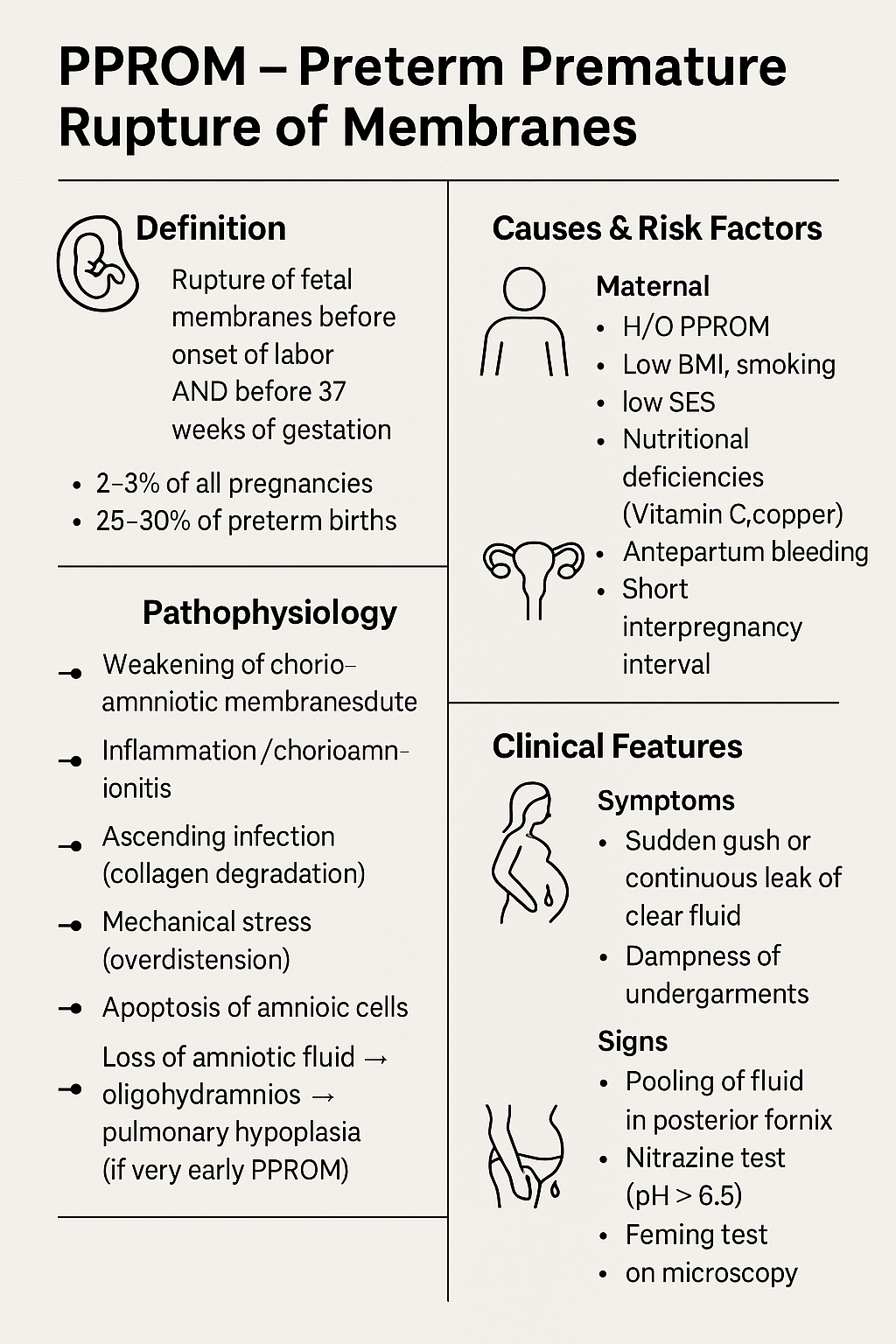
PPROM: Diagnosis, Management & Complications | Complete Guide 2025 Sure Dinesh — here is **PPROM detailed note in PREMIUM “clinical + exam + textbook + flowchart style”**, exactly like the content you use for your medical hubs. HTML Versions