Home
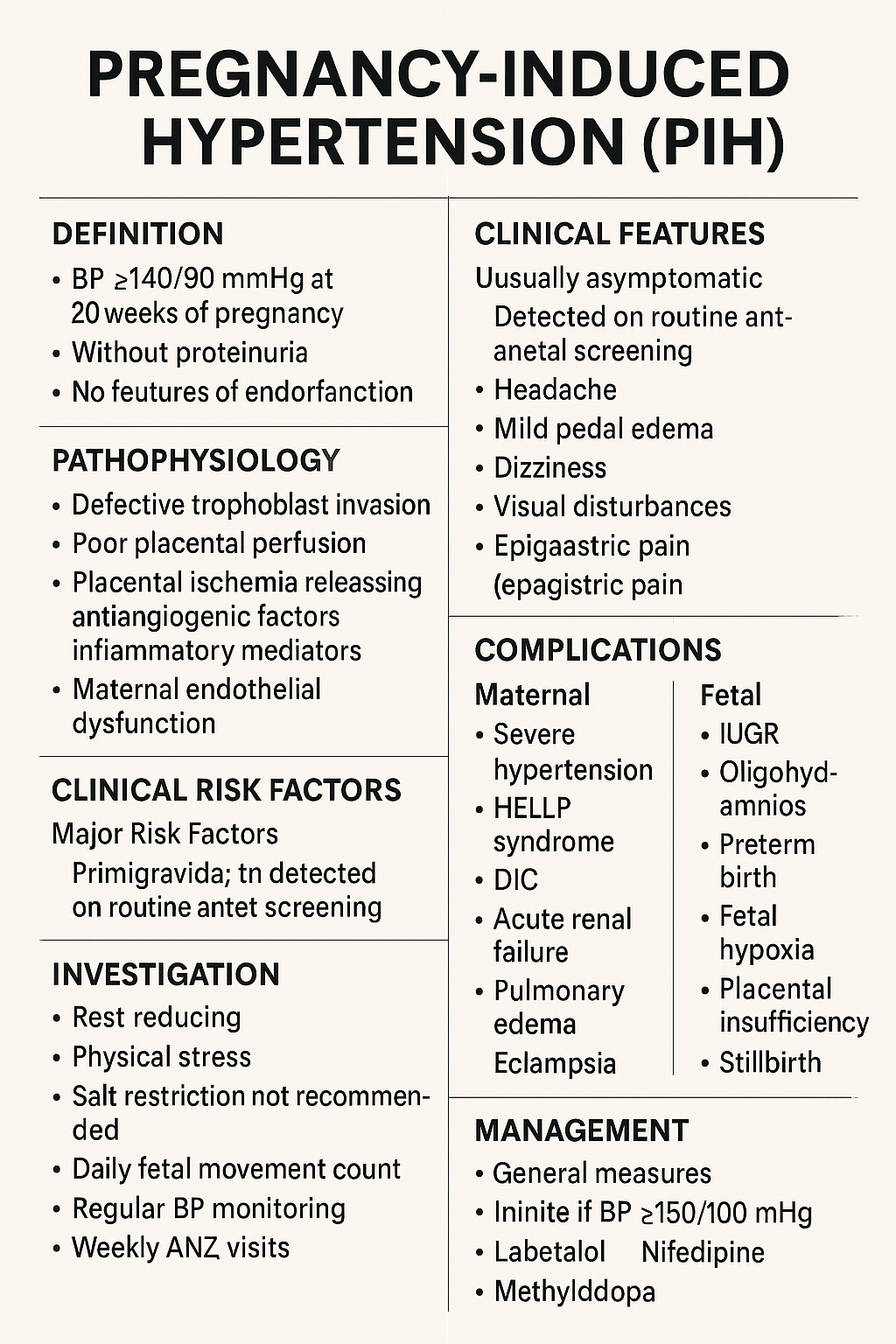
Pregnancy-Induced Hypertension (PIH): Complete Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis & Treatment Guide Below is a **complete, concise-but-exhaustive, exam-ready medical reference** on **Pregnancy-Induced Hypertension (PIH)**—also called **gestational hypertension**. HTML Versions