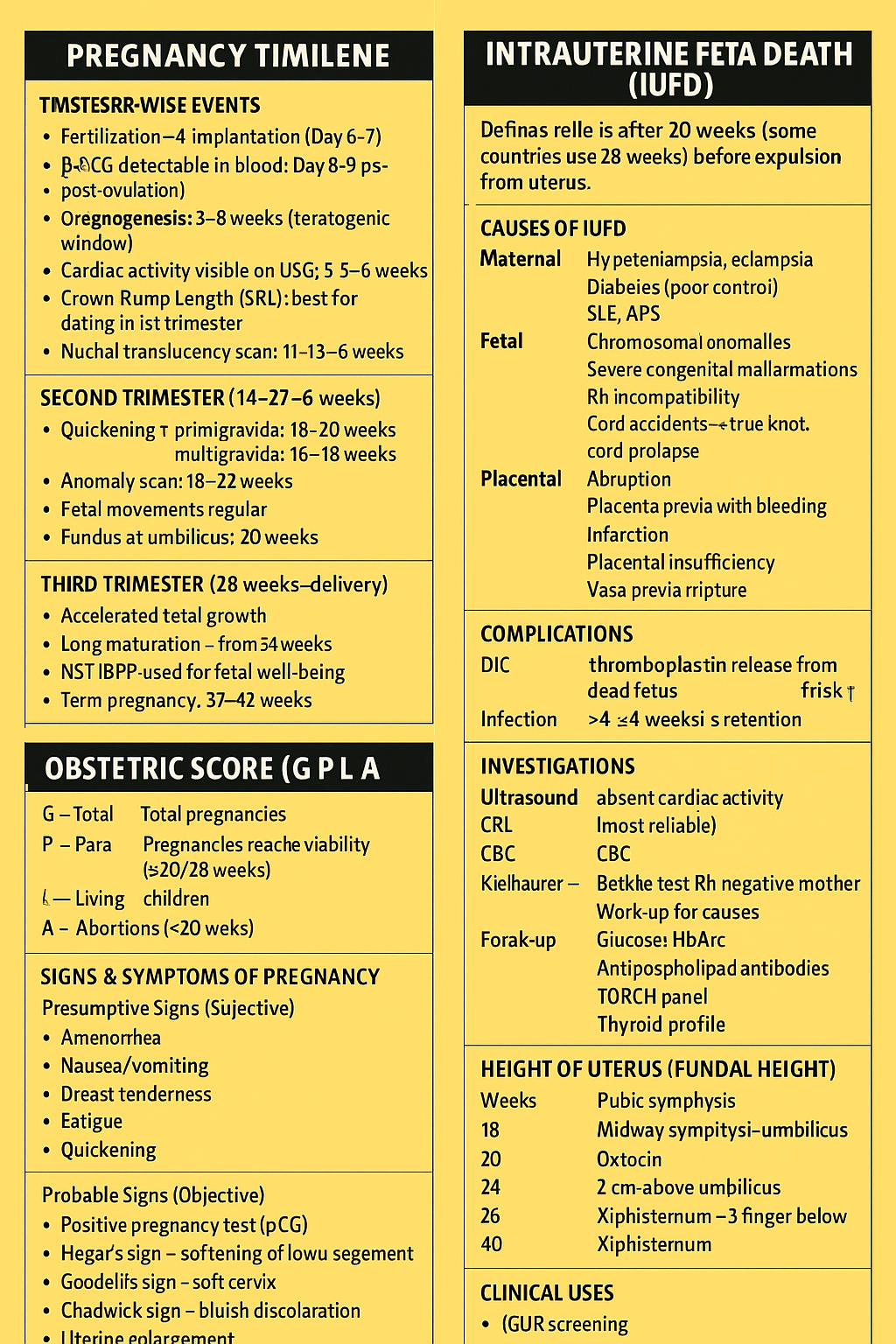
# ⭐ **1. Pregnancy Timeline (Trimester-wise Events)**
### **First Trimester (0–13+6 weeks)**
* Fertilization → Implantation (Day 6–7)
* β-hCG detectable in blood: **Day 8–9 post-ovulation**
* Organogenesis: **3–8 weeks** (teratogenic window)
* Cardiac activity visible on USG: **5.5–6 weeks**
* Crown-Rump Length (CRL): best for dating in 1st trimester
* Nuchal translucency scan: **11–13+6 weeks**
### **Second Trimester (14–27+6 weeks)**
* Quickening (primigravida: 18–20 weeks; multigravida: 16–18 weeks)
* Anomaly scan: **18–22 weeks**
* Fetal movements regular
* Fundus at umbilicus: **20 weeks**
### **Third Trimester (28 weeks–delivery)**
* Accelerated fetal growth
* Lung maturation – surfactant rise from **34 weeks**
* NST/BPP used for fetal well-being
* Term pregnancy: **37–42 weeks**
---
# ⭐ **2. Calculation of EDD (Estimated Date of Delivery)**
### **Naegele’s Rule**
If LMP is known:
**EDD = LMP + 1 year – 3 months + 7 days**
**Example:**
LMP = 10 August 2025
EDD = 17 May 2026
### **If Cycle Length ≠ 28 days**
Add/subtract the difference to LMP before applying Naegele’s rule.
### **By Ultrasound Dating**
* **CRL (6–13+6 weeks): MOST ACCURATE**
* If difference > **7 days**, revise EDD.
### **Second Trimester Formula (BPD, FL, HC, AC)**
Used when LMP is unknown, accuracy ±10 days.
---
# ⭐ **3. Intrauterine Fetal Death (IUFD)**
### **Definition**
Fetal death **after 20 weeks** (some countries use 28 weeks) **before expulsion from uterus**.
---
## **Causes of IUFD**
### **Maternal**
* Hypertension, preeclampsia, eclampsia
* Diabetes (poor control)
* SLE, APS
* Severe anemia
* Infections (TORCH, syphilis, malaria)
### **Fetal**
* Chromosomal anomalies
* Severe congenital malformations
* Rh incompatibility
* Cord accidents → true knot, cord prolapse
### **Placental**
* Abruption
* Placenta previa with bleeding
* Infarction
* Placental insufficiency
* Vasa previa rupture
---
## **Clinical Features**
* Absent fetal movements
* No fetal heart sounds
* Brownish discharge (spalding sign late)
---
## **Complications**
1. **DIC (Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation)**
* Due to thromboplastin release from dead fetus
* Risk ↑ after **>4 weeks retention**
2. **Infection**
3. Psychological impact on mother
---
## **Investigations**
* **Ultrasound** → absent cardiac activity (most reliable)
* **Coagulation profile** → PT, APTT, fibrinogen, D-dimer
* **CBC**
* **Kleihauer–Betke test** (Rh negative mother)
* **Work-up for causes:**
* Glucose, HbA1c
* Antiphospholipid antibodies
* TORCH panel
* Thyroid profile
---
## **Management**
### **If IUFD Confirmed**
* **Induction of labour** is recommended
* Misoprostol (dose per gestational age)
* Oxytocin
* If prior classical CS or scarred uterus → mechanical methods preferred.
### **Monitoring**
* Coagulation profile **every 12 hours**
* Blood products available
### **Do NOT do expectant management** beyond 1–2 days unless mother desires.
---
# ⭐ **4. Obstetric Score (G P L A)**
* **G – Gravida:** total pregnancies
* **P – Para:** pregnancies reaching viability (≥20/28 weeks)
* **L – Living children**
* **A – Abortions (<20 weeks)**
**Example:**
G4 P2 L2 A1 → Total 4 pregnancies, 2 delivered alive, 2 living, 1 abortion.
---
# ⭐ **5. Signs & Symptoms of Pregnancy**
### **Presumptive Signs (Subjective)**
* Amenorrhea
* Nausea/vomiting
* Breast tenderness
* Fatigue
* Quickening
### **Probable Signs (Objective)**
* Positive pregnancy test (β-hCG)
* Hegar’s sign – softening of lower uterine segment
* Goodell’s sign – soft cervix
* Chadwick sign – bluish discoloration
* Uterine enlargement
### **Positive Signs (Confirmatory)**
* Fetal heart sounds (Doppler 10–12 wks)
* Ultrasound showing fetus
* Palpation of fetal parts/movement by examiner
---
# ⭐ **6. Height of Uterus (Fundal Height)**
| Weeks | Fundal Height |
| ----- | ------------------------------ |
| 12 | Pubic symphysis |
| 16 | Midway symphysis–umbilicus |
| 20 | Umbilicus |
| 24 | 2 cm above umbilicus |
| 28 | Xiphisternum – 3 fingers below |
| 36 | Xiphisternum |
| 40 | Drops down due to lightening |
### **Clinical Uses**
* IUGR screening
* Polyhydramnios/Oligohydramnios identification
* Multiple pregnancy suspicion
* Growth chart plotting
---
# ⭐ **20 HARD CASE-BASED MCQs (HTML + CSS + JS Stylish Exam Mode)**
👉 **Copy–paste into a single .html file. Works offline.**
👉 **Shows answers with explanations.**
---
```html
Hardest 20 MCQs – Pregnancy Timeline, EDD, IUFD, Uterine Height
1. A woman with LMP 14 Feb 2025 presents for dating scan. CRL suggests 9w2d, differing from LMP by 10 days. What is the correct EDD?
A. Use LMP-based EDD only
B. Use USG-based EDD because difference >7 days
C. Average both values
D. Repeat USG after 2 weeks
Correct: B
In 1st trimester, revise EDD if difference >7 days.
2. IUFD diagnosed at 32 weeks. Fibrinogen is 120 mg/dL. Next step?
A. Expectant management
B. Immediate induction of labour
C. Cesarean section
D. Wait 1 week for spontaneous labour
Correct: B
Low fibrinogen indicates DIC risk → deliver early.
3. Fundal height is 34 cm at 28 weeks. Most likely diagnosis?
A. IUGR
B. Wrong dates
C. Polyhydramnios
D. Oligohydramnios
Correct: C
FH greater than expected → polyhydramnios/multiple pregnancy.
4. Woman presents with absent fetal movements. USG shows absent cardiac activity & overlapping skull bones. Diagnosis?
A. Missed abortion
B. IUFD with Spalding sign
C. Anencephaly
D. Severe IUGR
Correct: B
Spalding sign = overlapping skull bones → IUFD.
5. Quickening occurs at what gestational age in a primigravida?
A. 12 weeks
B. 14–16 weeks
C. 18–20 weeks
D. >22 weeks
Correct: C.
6. A woman at 20 weeks has bleeding and placenta previa. What risk increases?
A. IUFD due to abruption
B. IUFD due to fetal anemia
C. IUFD due to maternal hypotension
D. Both A & B
Correct: B
Placenta previa → fetal blood loss → anemia → IUFD.
7. Best investigation to diagnose IUFD?
A. NST
B. Doppler
C. Ultrasound with cardiac activity
D. CTG
Correct: C.
8. Uterine height at 36 weeks normally corresponds to:
A. Umbilicus
B. Xiphisternum
C. 2 cm below umbilicus
D. Above xiphisternum
Correct: B.
9. After IUFD, coagulation profile monitoring should be done every:
A. 4 hours
B. 6 hours
C. 12 hours
D. 24 hours
Correct: C.
10. A lady is G4P2L1A1. What does this mean?
A. 4 pregnancies, 2 viable births, 1 living child, 1 abortion
B. 4 pregnancies, 2 abortions, 1 living child
C. 4 pregnancies, 1 viable birth
D. None
Correct: A.
11. LMP unknown. CRL dates pregnancy at 11 weeks. EDD should be calculated using:
A. BPD only
B. CRL only
C. Symphysis-fundal height
D. Mix of parameters
Correct: B.
12. Which is a probable sign of pregnancy?
A. Quickening
B. Fetal heart sounds
C. Positive β-hCG test
D. Palpable fetal parts
Correct: C.
13. Woman with IUFD for 4 weeks is most at risk of:
A. Sepsis
B. PPH
C. DIC
D. Shock
Correct: C.
14. Fundal height lower than expected indicates:
A. IUGR
B. Polyhydramnios
C. Multiple gestation
D. Wrong dates >14 days
Correct: A.
15. Best step after IUFD diagnosis if cervix unfavorable?
A. Cesarean section
B. Misoprostol induction
C. Expectant waiting 1 week
D. Foley catheter + oxytocin
Correct: B.
16. Positive sign of pregnancy?
A. Chadwick sign
B. Hegar sign
C. Palpation of fetal movement by examiner
D. Amenorrhea
Correct: C.
17. Earliest detection of pregnancy is via:
A. TVS gestational sac
B. Urine test
C. Serum β-hCG
D. Fetal heart sounds
Correct: C.
18. Abruption leading to IUFD is mainly due to:
A. Fetal hypoxia
B. Amniotic fluid loss
C. Cord compression
D. Increased uterine tone
Correct: A.
19. EDD for LMP 1 Oct 2025:
A. 1 June 2026
B. 8 July 2026
C. 6 July 2026
D. 8 June 2026
Correct: C. (Add 7 days → 8 Oct → subtract 3 months → 8 July → +1 yr)
20. Cord accidents most strongly associated with:
A. Preterm labour
B. IUFD
C. Polyhydramnios
D. Multiple pregnancy
Correct: B.
```
---