Home
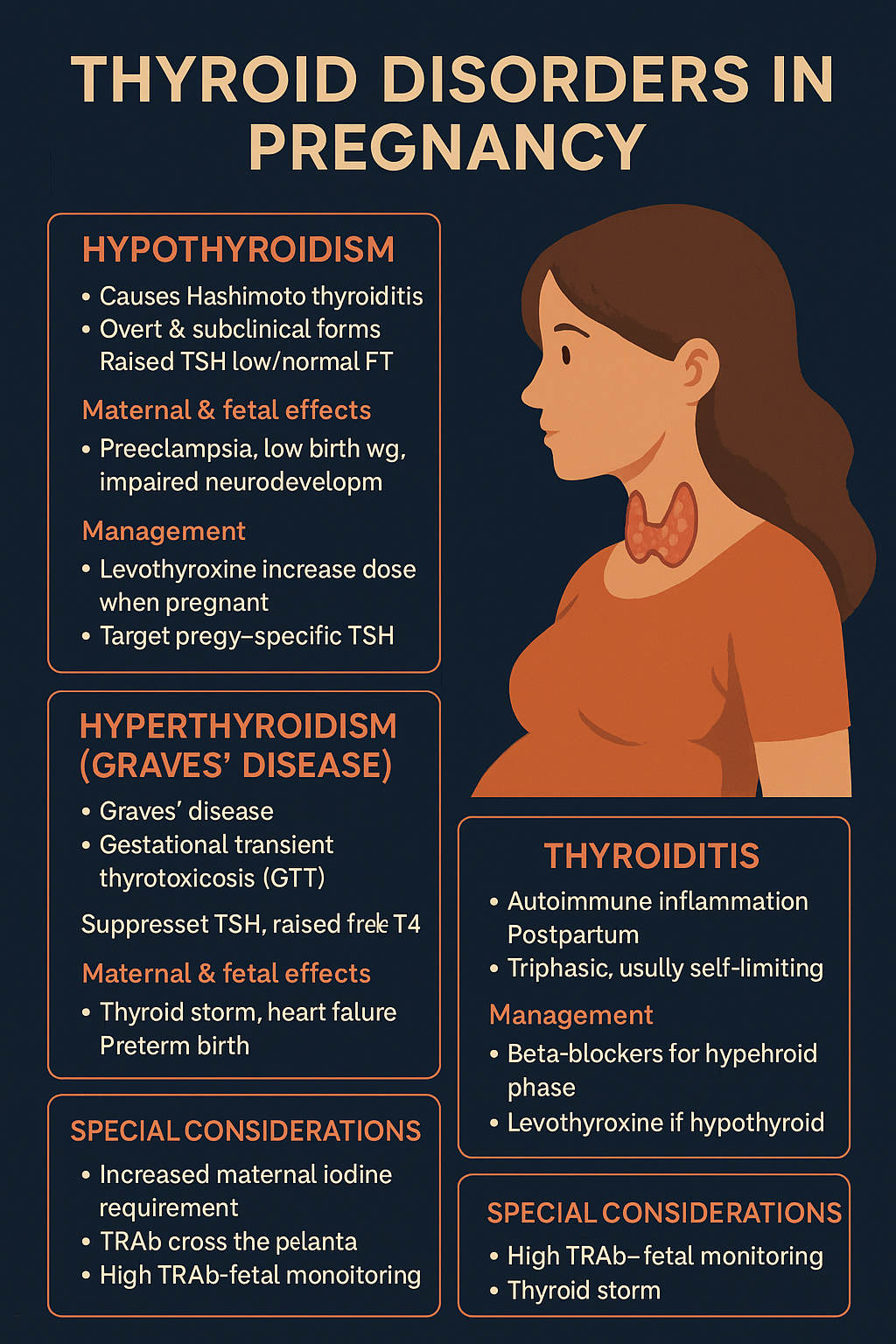
Thyroid Disorders in Pregnancy: Symptoms, Diagnosis, Risks & Treatment Guide (2025 Update) Below is a **complete, concise-but-exhaustive, exam-ready medical reference** for **Thyroid Disorders in Pregnancy**, covering **hypothyroidism, hyperthyroidism (Graves’), thyroiditis, and special considerations**. HTML Versions