Home
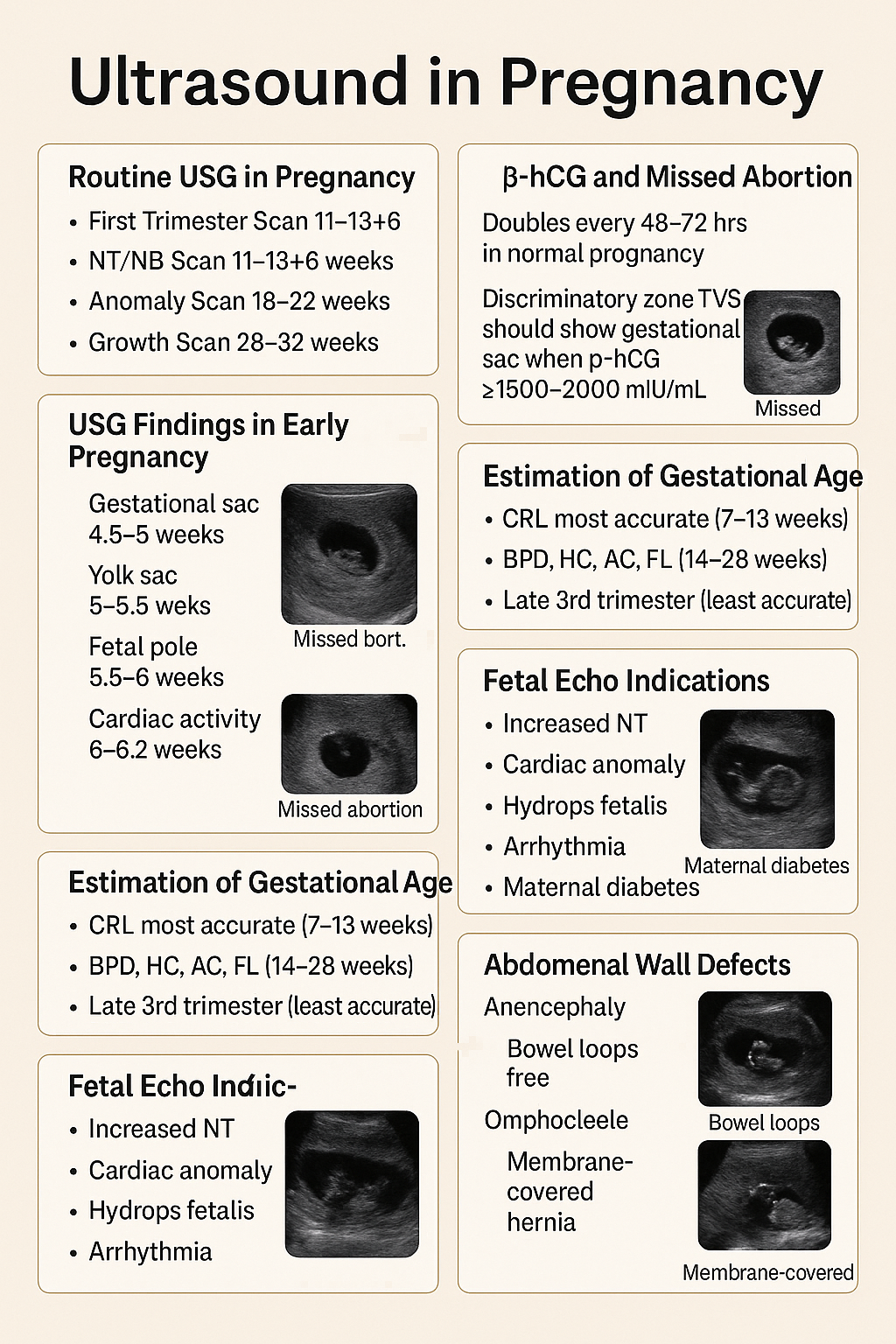
Ultrasound in Pregnancy: Early USG, β-hCG, Missed Abortion, Fetal Anomalies Guide 2025 --- HTML Versions