Home
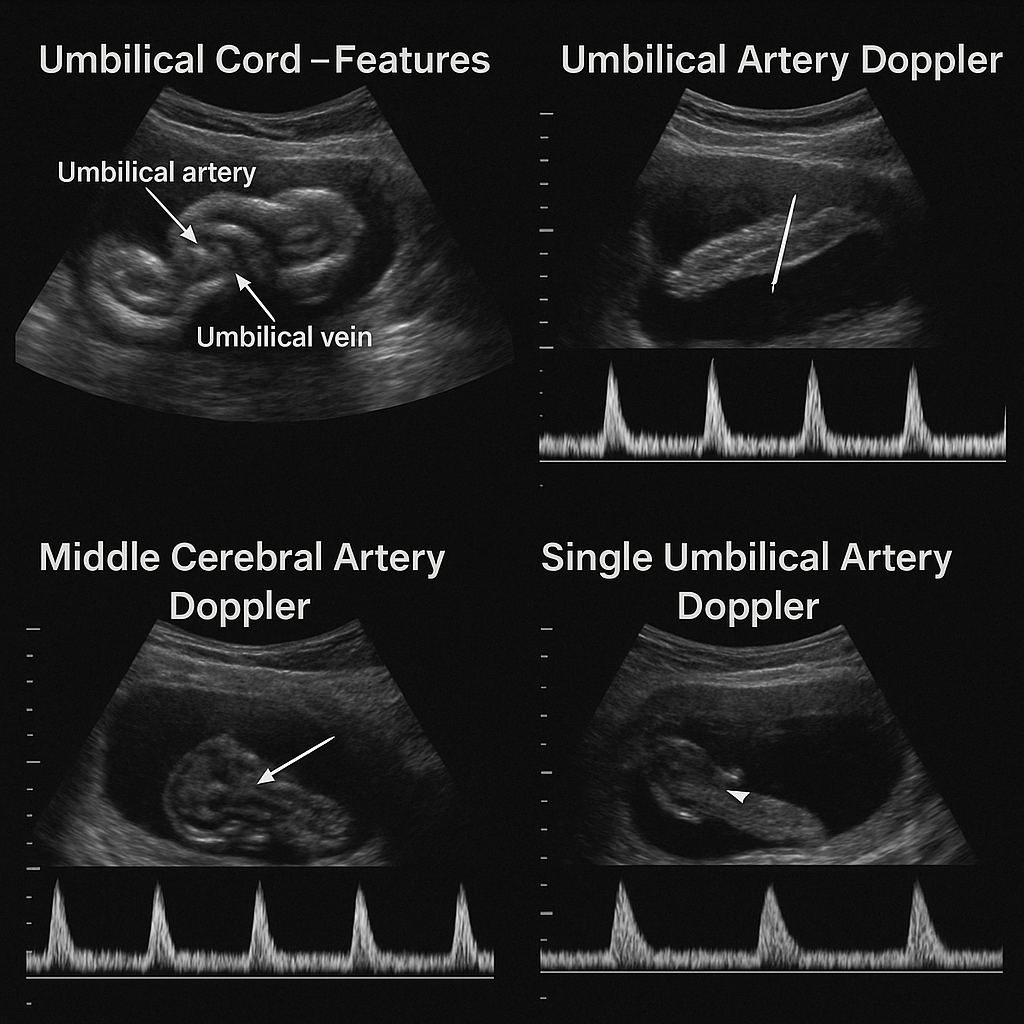
Umbilical Cord Features, UA & MCA Doppler, Single Umbilical Artery | Complete Obstetrics Doppler Guide 2025 --- HTML Versions